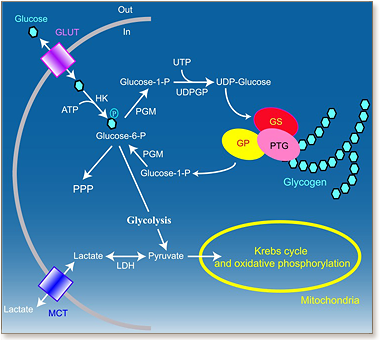
 In 1995 Benington and Heller formulated an energy hypothesis of sleep centered on a key role of glycogen. It was postulated that a major function of sleep is to replenish glycogen stores in the brain that have been depleted during wakefulness which is associated to an increased energy demand. Astrocytic glycogen depletion participates to an increase of extracellular adenosine release which influences sleep homeostasis. Here, we will review some evidence obtained by studies addressing the question of a key role played by glycogen metabolism in sleep regulation as proposed by this hypothesis or by an alternative hypothesis named “glycogenetic” hypothesis as well as the importance of the confounding effect of glucocorticoïds. Even though actual collected data argue in favor of a role of sleep in brain energy balance-homeostasis, they do not support a critical and direct involvement of glycogen metabolism on sleep regulation. For instance, glycogen levels during the sleep-wake cycle are driven by different physiological signals and therefore appear more as a marker-integrator of brain energy status than a direct regulator of sleep homeostasis. In support of this we provide evidence that blockade of glycogen mobilization does not induce more sleep episodes during the active period while locomotor activity is reduced. These observations do not invalidate the energy hypothesis of sleep but indicate that underlying cellular mechanisms are more complex than postulated by Benington and Heller.
In 1995 Benington and Heller formulated an energy hypothesis of sleep centered on a key role of glycogen. It was postulated that a major function of sleep is to replenish glycogen stores in the brain that have been depleted during wakefulness which is associated to an increased energy demand. Astrocytic glycogen depletion participates to an increase of extracellular adenosine release which influences sleep homeostasis. Here, we will review some evidence obtained by studies addressing the question of a key role played by glycogen metabolism in sleep regulation as proposed by this hypothesis or by an alternative hypothesis named “glycogenetic” hypothesis as well as the importance of the confounding effect of glucocorticoïds. Even though actual collected data argue in favor of a role of sleep in brain energy balance-homeostasis, they do not support a critical and direct involvement of glycogen metabolism on sleep regulation. For instance, glycogen levels during the sleep-wake cycle are driven by different physiological signals and therefore appear more as a marker-integrator of brain energy status than a direct regulator of sleep homeostasis. In support of this we provide evidence that blockade of glycogen mobilization does not induce more sleep episodes during the active period while locomotor activity is reduced. These observations do not invalidate the energy hypothesis of sleep but indicate that underlying cellular mechanisms are more complex than postulated by Benington and Heller.